《TAIPEI TIMES》 Enterovirus cases reach 10-year high
Centers for Disease Control Epidemic Intelligence Center Director Guo Hung-wei speaks at a news conference in Taipei yesterday. Photo: Lin Hui-chin, Taipei Times
TREND: This year’s epidemic did not follow the usual pattern of a peak in late May or early June, decreasing in summer and increasing again in autumn, an official said
/ Staff writer, with CNA
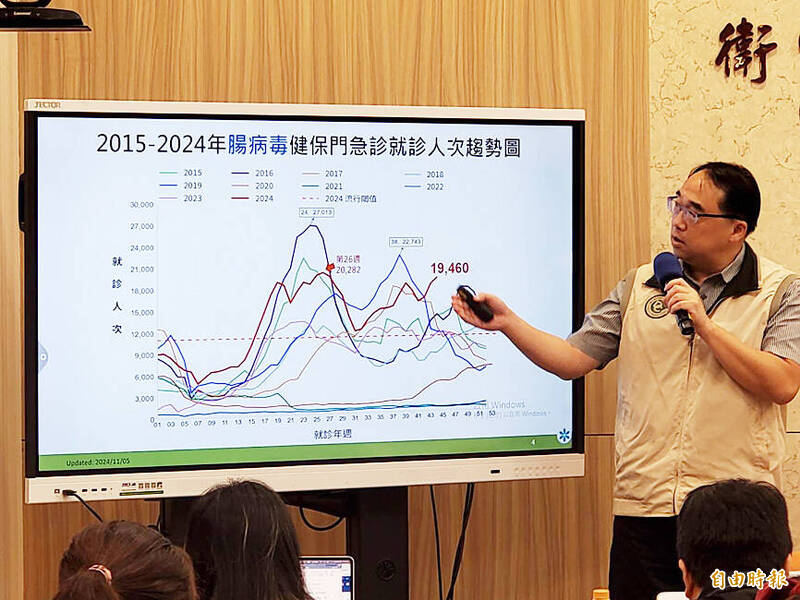
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) yesterday said that more than 19,000 cases of enterovirus infections were recorded from Oct. 27 to Saturday last week, the highest number for the period in the past 10 years.
Over those seven days, 19,460 people visited emergency departments or outpatient clinics due to enterovirus infections — a 4.7 percent week-on-week increase, CDC spokeswoman Tseng Shu-hui (曾淑慧) told a news conference.
“Enterovirus is highly contagious and is most easily spread in places with close contact and frequent interactions between people such as homes, kindergartens, daycare classes and childcare centers,” the CDC said in a statement.
This year’s unusually severe autumn-winter outbreak might be because many children were not exposed to a wide variety of virus strains during the COVID-19 pandemic, Tseng said.
The CDC spokeswoman said that 265 classes — 25 elementary-school classes, 186 kindergarten classes and 54 others — were suspended in the seven-day period.
The epidemic is expected to peak late this month, but cases would probably remain high through next month, she said.
“The usual seasonal pattern for enterovirus is that outbreaks occur from late March to early April, with the peak in late May to early June,” she said. “After the summer vacation, cases typically decrease, but tend to rise again in September with the start of the school year.”
“However, this year the epidemic persisted through the summer and surged in the autumn and winter, which is unusual,” she said.
The center urged parents to “implement good hygiene” such as washing hands with soap and water, and regularly disinfect home and learning environments.
The CDC said children under the age of five are at “high risk” of severe enterovirus infection, symptoms of which include drowsiness, low energy, weakness or paralysis of hands and feet, muscle twitching or contractions, persistent vomiting and shortness of breath.
“People should pay attention to the early warning signs of severe enterovirus in children” and take them to hospital as soon as possible if symptoms are detected, the CDC said.
新聞來源:TAIPEI TIMES



















